Computer Hardware Terms
| Top 10 hardware |
|---|
|
1. Computer
A computer is a programmable device that stores, retrieves, and processes data. The term “computer” was originally given to humans (human computers) who performed numerical calculations using mechanical calculators, such as the abacus and slide rule. The term was later given to a mechanical device as they began replacing the human computers. Today’s computers are electronic devices that accept data (input), process that data, produce output, and store (storage) the results.
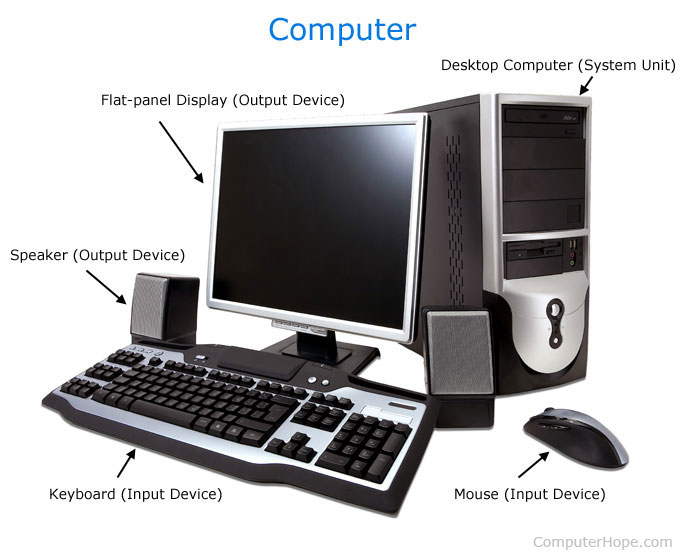
In the picture below, you can see the desktop computer, flat-panel display, speakers, keyboard, and mouse. We’ve also labeled each of the input devices and output devices. |
|
2. CPU
Alternately referred to as a processor, central processor, or microprocessor, the CPU (pronounced sea-pea-you) is the central processing unit of the computer. A computer’s CPU handles all instructions it receives from hardware and software running on the computer.
The CPU’s main function is to take input from a peripheral (keyboard, mouse, printer, etc) or computer program, and interpret what it needs. The CPU then either outputs information to your monitor or performs the peripheral’s requested task. Today, in addition to the different names of computer processors, there are different architectures (32-bit and 64-bit), speeds, and capabilities. |
|
3. Motherboard
The motherboard is a printed circuit board and foundation of a computer that is the biggest board in a computer chassis. It allocates power and allows communication to and between the CPU, RAM, and all other computer hardware components.
A motherboard provides connectivity between the hardware components of a computer, like the processor (CPU), memory (RAM), hard drive, and video card. There are multiple types of motherboards, designed to fit different types and sizes of computers. |
|
4. Sort Buttons
|
|
5. Drag and Drop
|
|
6. Status Bar
|
|
7. Paste from Clipboard
|
|
8. Add Bullet Points
|
|
9. Copy of Worksheet
|
|
10. Undo-Redo Buttons
|
| Formatting Tips |
|
11. Auto Format
|
|
12. Format Painter
|
|
13. Cell Message
|
|
14. Strikethrough
|
|
15. Barcode
|
|
16. Month Name
|
|
17. Highlight Blank Cells
|
|
18. Font Color with Custom Formatting
|
|
19. Theme Color
|
|
20. Clear Formatting
|
| Formula Tips |
|
21. Sentence Case
|
|
22. Random Numbers
|
|
23. Count Words
|
|
24. Calculate Age
|
|
25. Ratio
|
|
26. Root of Number
|
|
27. Days in Month
|
|
28. Month’s last Date
|
|
29. INDEX and MATCH
|
|
30. SUMPRODUCT IF
|
| Charting Tips |
|
31. Smooth Line
If you love to use a line chart, then you are awesome but it would be more awesome if you use a smooth line in the chart. This will give a smart look to your chart. Here are the steps:
|
|
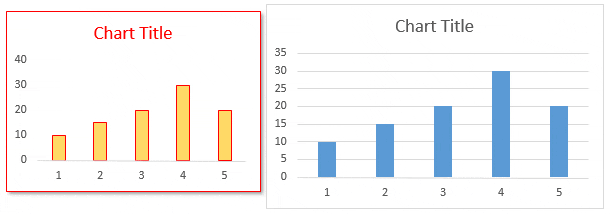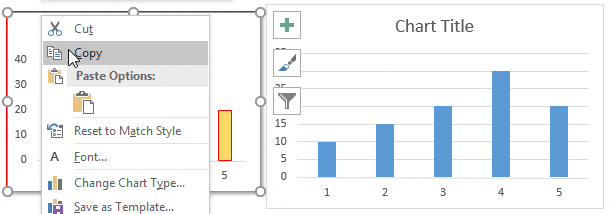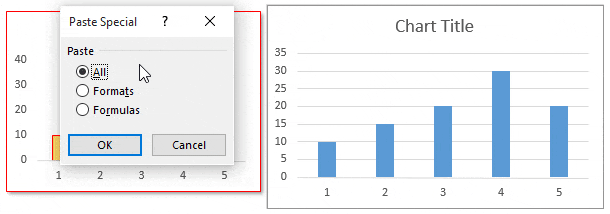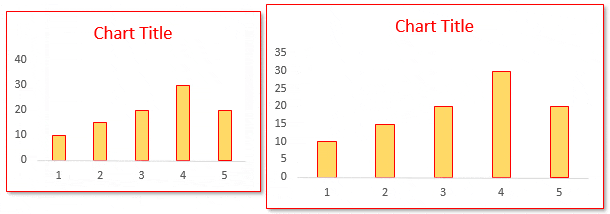
32. Chart Formatting
Steps to Copy Formatting from One Chart to Another:
|
|
33. Hide Axis Labels
This charting tip is simple but still quite useful. If you don’t want to show axis label values in your chart you can delete them. But the better way is to hide them instead of deleting. Here are the steps:
|
|
34. Display Units
If you are dealing with the large numbers in your chart, you can change the units for axis values. |
|
35. Round Corner
I often use Excel charts with rounded corners and if you like to use round corners too, here are the simple steps.
|
|
36. Hide Gap
Let’s say if you have a chart with monthly sales in which Jun has no amount and cell is empty. You can use the following options for that empty cell.
Here are the steps to use these options.
Make sure to use “Connect data points with the line” (recommended). |
|
37. Pictograph in Excel
If you know how to present data in an understandable and effective way, you can deliver your message strongly. It is the total employees in a company age wise and we need to present these groups using this chart.
Now our chart is ready to rock. Note: There is an option to specify unit/picture for the chart. You can use it if the values per bar in your chart are large (more than 20). The thing is that the picture icons will become smaller with more numbers and this option helps in that case. |
|
38. Chart Template
Let’s say if you have a favourite chart formatting which you want to apply every time you create a new chart. You can create a chart template to use it anytime in the future and steps are as follow.
|
|
39. Default Chart
You can use a shortcut key to insert a chart, but the problem is, it will only insert the default chart, and in Excel, the default chart type is “Column Chart”. So if your favourite chart is a line chart, then the shortcut is useless for you. But let’s conquer this problem. Here are the steps to fix this:
|
|
40. Hidden Cells
When you hide a cell from the data range of a chart, it will also hide that data point from the chart as well. To fix this, just follow these steps.
|
| Printing Tips |
|
41. Print Titles
Let’s say you have headings in your table, and you want to print those headings on every page you print. In this case, you can fix “Print Titles” to print those headings on each page.
|
|
42. Page Order
Specifying the page order is quite useful when you want to print large data.
|
|
43. Print Comments
If you use comments in your reports then you can print them as well. At the end of all printed pages, you can get a list of all the comments.
|
|
44. Scale to Fit
Sometimes we struggle to print entire data on a single page. In this situation, you can use the “Scale to Fit” option to adjust the entire data into a single page.
|
|
45. Custom Header-Footer
Instead of using the page number in the header and footer, you can also use a custom header and footer.
|
|
46. Center on Page
Imagine you have fewer data to print on a page. In this case, you can align it at the center of the page while printing.
|
|
47. Print Area
The simple way to print a range is to select that range and use the option “print selection”. |
|
48. Custom Margin
It will show all the margins applied and you can change them just by drag and drop. |
|
49. Error Values
You can replace all the error values while printing with a specific value (three other values to use as a replacement). Here are the steps:
I think using “Double minus sign” is the best way to present errors in a report while printing it on a page. |
|
50. Custom Start Page Number
If you want to start page number from a custom number let’s say 5. You can specify that number and rest of the pages will follow that sequence.
Important Note: This option will only work if you have applied header/footer in your worksheet. |
| Advanced Tips |
|
51. Tracking Important Cells
Sometimes we need to track some important cells in a workbook and for this, the best way is to use the watch window. In the watch window, you add those important cells and then get some specific information about them in one place (without navigating to each cell). Here are the steps to use it:
Once you hit OK, you’ll some specific information about the cell(s) in the watch window. |
|
52. Flash Fill
It’s like a copycat, perform the task which you have performed. Let me give you an example. Once you do this it will extract the month from the rest of the dates, just like below. |
|
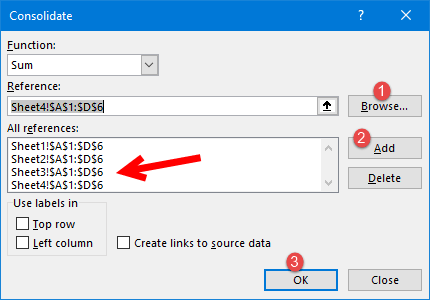
53. Combine Worksheets
I’m sure somewhere in the past you have received a file from your colleague where you have 12 different worksheets for 12 months data. In this case, the best solution is to combine all of those worksheets using the “Consolidate” option and here are the steps for this.
|
|
54. Live Image
In Excel, using a live image of a table can help you resize it according to space and to create a live image there are two different ways which you can use. One is camera tools and the second is the paste special option. Here the steps to use camera tool and for paste special use the below steps.
Make sure to read this guide about camera tool to learn more about linked images. |
|
55. Protect a Workbook
Adding a password to a workbook is quite simple, here are the steps.
Now, whenever you re-open this file it will ask you to enter the password to open it. |
|
56. Userform
A few of the Excel users know that there is a default data entry form is there which we can use. And the best part is there is no need to write a single line of code for this.

|
|
57. Custom Tab
We all some favorite option or some options which we use frequently. To access all those options in one place you create tab and add them to it. Follow these steps:
Now you are a new tab in the Excel ribbon with all the favorite options. |
|
58. Goal Seek
In simple words, Goal Seek is a problem-solving tool. It helps you find the input value by proving the value you want in the result. |
|
59. Text to Speech
This is an option where you can make Excel speak the text you have entered into a cell or a range of cells.
|
|
60. Named Range
To create a named the range the easiest method is to select the range create it using the “Create from Selection” option. Here are the steps to do this:
|
| Data Cleansing Tips |
|
61. Trim
TRIM can help you to remove extra spaces from a text string. Just refer to the cell from where you want to remove the spaces and it will return the trimmed value in the result. |
|
62. Remove Duplicates
One of the most common things which we face while working with large data is “Duplicate Values”. In Excel, to remove these duplicate values is quite simple. Here’s how to do this.
Once you click OK, Excel will remove all the rows from the selected data where values are duplicate and show a message with the number of values removed and unique values left. |
|
63. Combine Text (Fill Justify)
I know five different ways to merge text from a range but out of those Fill Justify is my favorite. It’s one of the less used options in Excel, but worth not to be missed for any reason. Let say you have words in the range A1: A5 and you want to concatenate all of them in a single cell. Here’s how to do this with fill justify.
It combined the text from range A1:A5 to cell A1. |
|
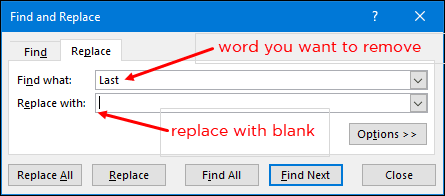
64. Remove Specific Character
Let’s say you have some text values in a column and from those values you want to replace a specific character or a word… You can do this simply by find and replace option. Let say you have words in the range A1: A5 and you want to concatenate all of them in a single cell. Here’s how to do this with fill justify.
The moment you click on “Replace All” Excel will remove that particular character from the entire column. |
|
65. Combine Text
So, you have text in multiple cells, and you want to combine all the text into one cell. No, this time not with fill justify. We are doing it with TEXT JOIN. If you use Office 365, there is new function TEXTJOIN which is a game changer when it comes to the concatenation of text. TEXTJOIN(delimiter, ignore_empty, text1, [text2], …) All you need to do is to add a delimiter (if any), and TRUE if you want to ignore empty cells, and in the end, refer to the range. |
|
66. Unpivot Data
Look at the below table you can use it as a report but can use you use it further as a raw data. No, you can’t. But if you convert this table in something like below you can use it easily anywhere. |
|
67. Delete Error Cells
Mostly while working with large data it obvious to have error values but it’s not good to keep them. The easiest way to deal with these error values is select them and delete them and these are the simple steps.
Once you click OK it will select all the errors and then you can simply delete all by using “Delete” button. |
|
68. Arrange Columns
Let’s say you want to arrange columns from the data using a custom order. The normal way is to cut and paste them one by one. But we also have an out of the box way. |
|
69. Convert to Date
Sometimes you have dates which are stored as text and you can use them in a calculation and further analysis. To simply convert them back to valid dates you can use DATEVALUE function… |
|
70. Negative to Positive

|
| Mouse Tricks |
|
71. Format Painter
Before I started to use format painter for applying cell formatting, I was using paste special with the shortcut key. Here’s how to do this:
|
|
72. Rename a Worksheet
I always found it quicker than using a shortcut key to change the name of a worksheet. All you have to do is just double click on the sheet tab and enter a new name. |
|
73. Fill Handle
I am sure shortcut addicts always use a shortcut key to drag formulas and values in downward cells. But using a fill handle is more impressive than using a shortcut key.
This method only works if you have values in corresponding column and it works only in the vertical direction. |
|
74. Hide Ribbon
If you want to work in a distraction-free mode, you can do this by collapsing your Excel ribbon. |
|
75. Edit a Shape
You often use shapes in our worksheets to present some messages and you have to insert some text into those shapes. Besides the typical method, you can use double click to edit a shape and insert the text into it. |
|
76. Column Width
Whenever you have to adjust column width you can double click on the right edge of the column header. It auto sets the column width according to the column data. |
|
77. Go to the Last Cell
This trick can be useful if you are working with a large dataset. By using a double click, you can go to the last cell in the range which has data. |
|
78. Chart Formatting
If you use Control + 1 to open formatting options to format a chart, then I bet you’ll love this trick. All you have to do is just make a double-click on the border of the graph to open formatting option. |
|
79. Pivot Table Double Click
Let’s say someone sent you a pivot table without the source data. As you already know Excel stores data in pivot cache before creating a pivot table. |
|
80. Right Click Menu
There is a right-click drop-down menu in Excel which few users know about. To use this menu all you need to do is select a cell or a range of the cell and then right-click and while holding it, drop the selection to somewhere else. |
| One Time Set-Up Tips |
|
81. Default File Saving Location
Normally while working on Excel I create more than 15 Excel files every day. And, if I save each of these files to my desktop it looks nasty. To solve this problem, I have changed my default folder for saving a workbook and here’s you can do this.
|
|
82. Disable Start Screen
I’m sure just like me you hate when you open Microsoft Excel (or any other Office app) and you see the start pop-up screen. It takes time depending on your system’s speed and add-ins you have installed. Here are the steps to disable the start-up screen in Microsoft Office.
From now onward, every time when you start Excel it will directly open the workbook without showing the start-up screen. |
|
83. Developer Tab
Before you start writing VBA codes the first thing you need to do is to enable “Developer Tab”. When you first install Microsoft Excel, developer wouldn’t be there. So, you need to enable it from settings.
Now when you come back to your Excel window, you’ll have a developer tab on the ribbon. |
|
84. Enable Macros
When you open a macro-enabled file, you need to enable macro options to run VBA codes. Follow these simple steps:
|
|
85. AutoCorrect Option
With the auto correct option, you can tell Excel to change a text string into another when you type it. Follow these simple steps:
|
|
86. Custom List
Just think like this, you have a list of 10 products which you sell. Whenever you need to insert those product name you can insert them using a custom list. Let me tell you how to do this:
Now, to enter the custom list you have just created, enter the first entry of the list in cell and then drill down that cell using fill handle. |
|
87. Apply Table
If you use pivot tables a lot then it’s important to apply the table to the raw data. With a table, there is no need to update the pivot table’s data source and it drag-down formulas automatically when you add a new entry. |
|
88. Gridline Color
If you are not happy with the default color of cell grid-lines then you can simply change it with a few clicks and follow these simple steps for this:
|
|
89. Pin to Taskbar
This is one of my favorite one-time set up to save time in the long run. The thing is instead of going to start menu to open Microsoft Excel, the best way is to pint it to the task-bar. |
|
90. Macro to QAT
If you have a macro code which you need to use frequently. Well, the easiest way to run a macro code is to add it to the quick access toolbar.
|
| Time Saver Tips |
|
91. Select Formula Cells
Let’s say you want to convert all the formulas into values and the cells where you have formulas are non-adjacent. So instead of selecting each cell one by one, you can select all the cells where you have a formula. Here are the steps:
|
|
92. Multiply using Paste Special
To do some one-time calculations you can use paste special option and save yourself from writing formulas. |
|
93. Highlight Duplicate Values
Well, you can use a VBA code to highlight values but the easiest way is to use conditional formatting. Here are the steps you need to follow:
Once you click OK, all the values which are duplicate will get highlighted. |
|
94. Quick Analysis
If you ever noticed that when you select a range of cell in Excel, a small icon at the bottom of the selection appears. This icon called “Quick Analysis”. |
|
95. RUN Command
you can also open your Excel application using RUN command.
|
|
96. Open Specific File
I’m sure like me you also have few or maybe one those kinds of workbooks which you open every day when you start working on Excel. There is an option in Excel which you can use to open a specific file(s) every time when you start Excel in your system. Here are the steps.
|
|
97. Open Excel Automatically
|
|
98. Smart Look Up
|
|
99. Screen Clipping
|
|
100. Locate a Keyboard Shortcut
|